
Local currency government bonds in Latin America and South Africa had a strong year in 2025, while major Asian countries lagged the broader market.
For local currency emerging-markets government debt, 2025 was a year to shine. This category returned 3.7 percent to investors (in euro) versus the developed-market Bloomberg Global Aggregate Government Bond index’s negative 5.7 percent. Amongst the best performers were benchmark heavyweights Brazil, Mexico and South Africa with the likes of India and China amongst the bottom performers. Divergent monetary policies, political regimes, tariff impacts and investor sentiment separated the winners from the losers. Within the Morningstar Category Global Emerging Markets Bonds – Local Currency, NinetyOne and Morgan Stanley have analyst-rated strategies on offer to investors.
People
NinetyOne’s Emerging Markets Local Currency Debt strategy continues to benefit from a highly seasoned and deeply cohesive leadership team, earning it a People Pillar Rating of Above Average. Lead manager Werner Gey van Pittius, at the helm since 2012, is supported by Antoon de Klerk (since 2017) and Christine Reed (promoted in 2023). This sovereign debt and currency team, in total 12 investors across Cape Town and London, have a long history of shared decision-making and boast roughly two decades of average experience. This team’s turnover is notably low compared to peers.
By contrast, MS INVF Emerging Markets Local Income holds a People Pillar rating of Average. The strategy’s portfolio management roster underwent significant turnover between 2021 and 2023, including departures of long-standing leaders. Current co-leads Brian Shaw Patrick Campbell stepped up as lead managers in mid-2023, after serving as comanagers since 2021 and 2022, respectively. Although both have lengthy firm tenures, they had limited portfolio-manager responsibilities before this strategy. Whilst the team has broadened its roster of idea generators, this remains a newer group compared with a cohort of strong peers. Continued stability will be key to proving long-term durability.
Process
NinetyOne’s approach earns an Above Average Process Pillar Rating, reflecting its disciplined blend of top-down macro signals and bottom-up country research. The team targets 150 bps of annual outperformance versus the JPM GBI-EM Global Diversified Index, driven mainly by active currency and interest-rate calls. Proprietary country models assess inflation, devaluation risks, and balance-sheet dynamics, feeding into a weekly asset-allocation scorecard that guides 20–30 active country over- and underweights. The team’s willingness to enter frontier and off-benchmark markets has historically added value, though it introduces episodic volatility.
Morgan Stanley’s process receives an Average Process Pillar Rating. Its decentralized structure gives eight portfolio managers authority to run individual risk books, with ideas pooled across vehicles. The investable universe stretches far beyond local sovereigns including hard-currency debt (capped at 40 percent) and corporate debt (limited to 10 percent). Emphasis is on bottom-up idea generation with limited top-down decisions aside from the managers aiming to keep the portfolio’s overall sensitivity to credit risk and interest rate changes close to the benchmark’s level. Derivative instruments frequently lift the portfolio’s notional exposure to 120–150 percent, occasionally as high as 165 percent, as the team aim to mimic the benchmark’s volatility profile. This high-conviction approach offers promise, but maintaining consistent execution over time is challenging, particularly amidst high team turnover.
Portfolio
NinetyOne’s country exposures are sized according to liquidity, valuation, and risk. The team’s familiarity with frontier markets is a strong differentiator which has benefited investors over time. For instance, by late 2024, the portfolio held and off-benchmark 8 percent stake in B rated and CCC rated bonds, including Ghana and Zambia, which the managers preferred owing to debt restructuring efforts. At that time, duration was slightly longer than the benchmark’s, with notable overweightings in Czech Republic and China, and an underweighting in China owing to geopolitical risk.
MS INVF’s portfolio is more aggressive and structurally less benchmark-tethered. It invests across local and hard-currency sovereigns, corporates, and frontier debt. Country weights can differ substantially. Large positions in markets such as Egypt, Uzbekistan, and Turkey often define short-term outcomes. Frontier allocations have historically ranged from 20 percent to 80 percent. Significant country deviations offer upside in recoveries but amplify dispersion when markets turn.
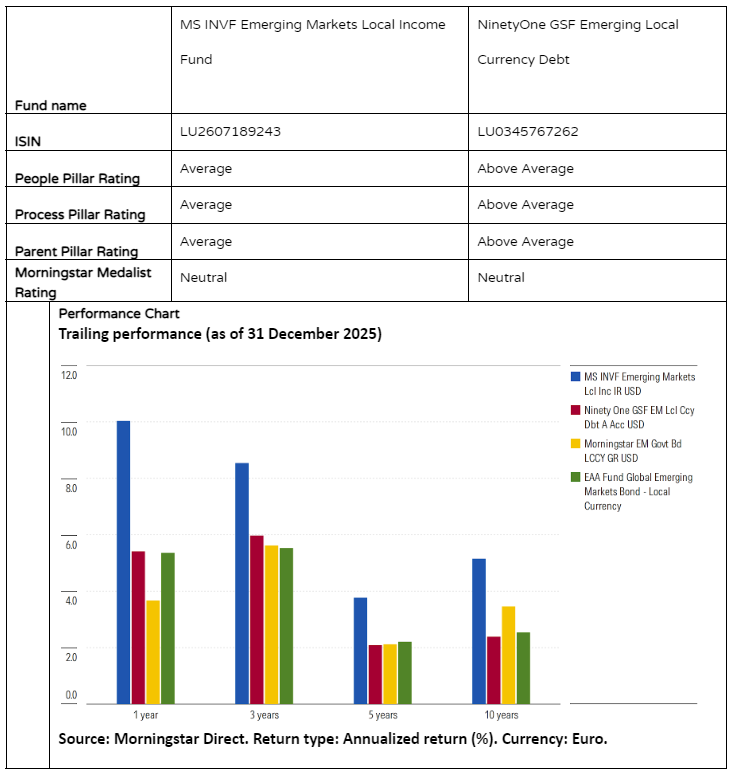
Performance
NinetyOne has delivered strong long-term results. The strategy tends to lag in sharp risk-off phases but captures rebounds effectively. Recent contributors include an underweight in Mexican bonds in 2024 as well as well-timed positions in the Egyptian pound and Turkish lira. In 2023, a sizeable Brazilian duration overweight supported returns that year as interest rates were cut. In 2025, the overweighting to Mexican bonds, were additive to performance.
At Morgan Stanley, the strategy’s credit and currency profile can make it more vulnerable during emerging-markets local-currency selloffs. For instance, an off-benchmark position in Sri Lanka hurt performance in 2018. On the other hand, off-benchmark frontier exposures and leveraged currency positions contributed meaningfully to the strategy’s rebound from 2023 into mid-2025, particularly its overweightings in Turkey and large off-benchmark stakes in Egypt, and Uzbekistan (collectively soaking up almost a third of assets mid 2024). Off-benchmark stakes and selective currency bets were beneficial to performance in 2025.
Elbie Louw CFA CIPM is a senior analyst in manager research at Morningstar Benelux. Morningstar is a member of the Investment Officer expert panel.